Assistant Programmer -2014
Ministry of Education
Q-1.What is Routing ? Difference between static and dynamic routing, provide their relative advantages and disadvantages .
Ans: Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in
a network or between or across multiple networks.
Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public
switched telephone network (PSTN),
and computer networks, such as the Internet.
BASIS FOR COMPARISON STATIC ROUTINGDYNAMIC ROUTING
|
Configuration |
Manual |
|
Automatic |
|
Routing table building |
Routing locations are hand-typed |
|
Locations are dynamically filled in the
table. |
|
Routes |
User defined |
|
Routes are updated according to change in
topology. |
|
Routing algorithms |
Doesn't employ complex routing algorithms. |
|
Uses complex routing algorithms to perform
routing operations. |
|
Implemented in |
Small networks |
|
Large networks |
|
Link failure |
Link failure obstructs the rerouting. |
|
Link failure doesn't affect the rerouting. |
|
Security |
Provides high security. |
|
Less secure due to sending broadcasts and
multicasts. |
|
Routing protocols |
No routing protocols are indulged in the
process. |
|
Routing protocols such as RIP, EIGRP, etc
are involved in the routing process. |
|
Additional resources |
Not required |
|
Needs additional resources to store the
information. |
Q-2.
Difference between 2G and 3G wireless technologies.
ans:
|
Parameters |
2G |
3G |
|
Name |
2nd
Generation Mobile Network |
3rd
Generation Mobile Network |
|
Introduced
in year |
1993 |
2001 |
|
Location
of first commercialization |
|
Japan |
|
Technology |
IS-95,
GSM |
IMT2000,
WCDMA |
|
Multiple
Address/Access system |
TDMA,
CDMA |
CDMA |
|
Switching
type |
Circuit
switching for Voice and Packet switching for Data |
Packet
switching except for Air Interface |
|
Speed
(data rates) |
14.4
Kbps |
3.1
Mbps |
|
Internet
service |
Narrow
band |
Broadband |
|
Special
Characteristic |
Digital
version of 1G technology |
Digital
broadband, speed increment |
|
Applications |
Voice
calls, Short messages, browsing (partial) |
Video
conferencing, mobile TV, GPS |
Q-3.Compare
virtual circuits and datagram networks
Following are the
important differences between Virtual Circuits & Datagram Networks −
|
Sr. No. |
Key |
Virtual
Circuits |
Datagram
Networks |
|
1 |
Definition |
Virtual Circuit is the connection oriented service in
which there is a implementation of resources like buffers, CPU, bandwidth,
etc., used by virtual circuit for a data transfer session. |
On other hand Datagram is the connection less service
where no such resources are required for the data transmission. |
|
2 |
Path |
In Virtual circuits as all the resources and bandwidth get
reserved before the transmission, the path which is utilized or followed by
first data packet would get fixed and all other data packets will use the
same path and consume same resources. |
On other hand in case Datagram network, the path is not
fixed as data packets are free to decide the path on any intermediate router
on the go by dynamically changing routing tables on routers. |
|
3 |
Header |
As there is same path followed by all the data packets, a
common and same header is being used by all the packets. |
On other hand different headers with information of other
data packet is being used in Datagram network. |
|
4 |
Complexity |
Virtual Circuit is less complex as compared to that of
Datagram network. |
However on other hand Datagram network are more complex as
compared to Virtual circuit. |
|
5 |
Reliability |
Due to fixed path and assurance of fixed resources,
Virtual Circuits are more reliable for data transmission as compared to
Datagram network. |
On other hand Datagram network due to dynamic resource
allocation and follow dynamic path is more prone to error and is less
reliable than Virtual circuits. |
|
6 |
Example and Cost |
Virtual circuits are costlier in installation and
maintenance and are widely used by ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Network,
which is used for the Telephone calls. |
On the other hand Datagram network are cheaper as compared
to the Virtual Circuits and are mainly used by IP network, which is used for
Data services like Internet. |
Q-4.Show
the ip address formats of class A, Class B and Class C Networks.
Ans:
IP (Internet
Protocol) is the fundamental protocol for communications on the Internet. It specifies the way information is packetized, addressed, transferred, routed, and received by networked devices.
|
Class |
Address range |
Supports |
|
Class A |
1.0.0.1 to
126.255.255.254 |
Supports 16 million
hosts on each of 127 networks. |
|
Class B |
128.1.0.1 to
191.255.255.254 |
Supports 65,000 hosts on
each of 16,000 networks. |
|
Class C |
192.0.1.1 to
223.255.254.254 |
Supports 254 hosts on
each of 2 million networks. |
|
Class D |
224.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255 |
Reserved for multicast groups. |
|
Class E |
240.0.0.0 to
254.255.255.254 |
Reserved for future use,
or research and development purposes. |
Q-5.What
is OSI Model? How do you describe application protocol and networking protocol?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual model created by the International Organization for Standardization which enables diverse communication systems to communicate using standard protocols.
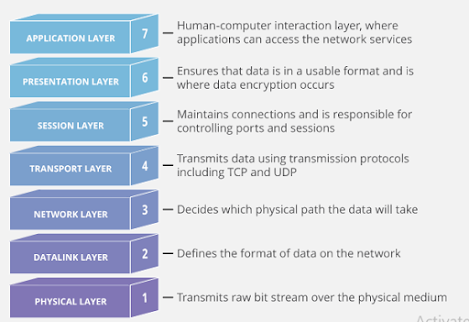
Ans:Data
Modeling:
Data modeling is a technique to document a software system using diagrams and symbols. It is used to represent communication of data.
The highest level of abstraction for the data model is called the Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD). It is a graphical representation of data requirements for a database.
Entity
Relationship Diagram
The main value of carefully constructing an ERD is that it can readily be converted into a database structure.
There are three components in ERD.
Entities: Number of tables you need for your database.
Attributes: Information such as property, facts you need to describe each table.
Relationships: How tables are
linked together. There are four types of relationships:
1. One to One
2. One to Many
3. Many to One
4. Many to Many
Q-7.Write
a computer program(C/C++) that takes a positive integer N as input and find out
the sum of the digits repeatedly until the result is converged to a single
digit: sample input : N=254189, Sample output=29(first steps), 11(second
steps), 2 (final step).
Ans:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
intn,sum=0,rem,
i=0;
printf("Enter
a number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n>0)
{
while(n!=0)
{
rem=n%10;
sum=sum+rem;
n=n/10;
}
if(sum>9)
{
i++;
printf("
Step %d: %d", i, sum);
n=sum;
sum=0;
}
}
printf("
Final Step Result: %d", sum);
return
0;
getch();
}
Q-8.Write
the following program using an object oriented programming language (C++/Java):
You are given the list of rolls, names and contact phones of all students in
your class as input.you have to write a
program to shorten the list in lexicographical order of names.
Ans:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace std;
class
student
{
public:
stringname,mobile;
int roll;
bool
operator<(student obj)
{
return
name<obj.name;
}
};
int main()
{
student
record[100];
int n;
cin>>n;
for(inti
=0; i<n;i++)
{
cin>>record[i].roll>>record[i].name>>record[i].mobile;
}
sort(record,record+n);
for(inti
=0; i<n;i++)
{
cout<<record[i].roll<<
" "<<record[i].name<< " "<<record[i].mobile<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Q-9.Write
an algorithm to find the shortest path from a source node S to destination node
D on a given graph G (V, E, and W). Here V is the set of vertices.E is the set
of edges and W is the set of weights associated with edges.
Q-10.Design
and E-R diagram for airline reservation system consisting of flights,
aircrafts, airports, fares, reservations , tickets, pilot, crew, and
passengers.Clearly highlight the entities, the primary key and mapping
cardinalities.
Q-11.What is digital divide? How do you can reduce the digital divide in Bangladesh and establish digital Bangladesh.
Digital divide:
The digital divide is the gap that exists between individuals who have access to modern information and communication technology and those who lack access. There are three key stages that influence digital inequality worldwide.
Digital inequality is evident between communities living in urban areas and those living in rural settlements; between socioeconomic groups; between less economically developed countries and more economically developed countries; between the educated and uneducated population.
3 Types of Digital Divide
There are numerous types of the digital divide that influence our efforts in accessing the internet. Some of the vivid gaps in digital inequality include:
1. Gender Divide
2. Social Divide
3. Universal Access Divide







0 মন্তব্যসমূহ